Contact Dermatitis is One of the Most Common Causes of Red, Itchy Rashes
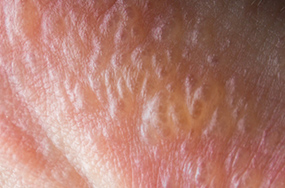 Contact dermatitis is an allergic reaction affecting areas of the skin, which becomes red, itchy and inflamed after contact with certain substances.
Contact dermatitis is an allergic reaction affecting areas of the skin, which becomes red, itchy and inflamed after contact with certain substances.
Blisters also may form on the skin. Later these areas will ooze, thicken and crack. Contact dermatitis differs from "dishpan hands" because "dishpan hands" is an irritant reaction, not an allergic reaction. The most common cause of contact dermatitis is poison ivy. Other causes are: Other plants, cosmetics, medications, metals, and chemicals.
What is poison ivy?
Poison ivy belongs to the plant family Anacardiaceae. Other members of this family include poison oak and sumac.
What happens when the skin comes in contact with poison ivy?
An oil resin, called urushiol (u-ru-she-ol), found in the plant's sap, causes the reaction. The response is usually not immediate and can occur 24 to 48 hours after contact has been made.
First, the skin becomes red followed by the development of bumps and blisters. Itching and swelling also may be present. After several days, the blisters break, releasing watery liquid. The blisters then begin to heal. Neither the liquid from the blister nor scratching the area will spread the rash.
Who is affected by contact dermatitis?
At least 7 out of 10 people could develop dermatitis if exposed to large amounts of poison ivy, oak or sumac. If contact is made through an accidental brief incident, 5 out of 10 people could experience a reaction. Adults are affected more often than very young children. Heredity has not yet been shown to play a role in predicting which family members are more likely to suffer reactions than others.
Treatments for dermatitis
Clean skin and clothing with soap and water to remove the urushiol resin. This will help to prevent the development of a rash. Also wash other objects that have been in contact with the resin. This will prevent re-exposure. Excessive scratching could cause a bacterial infection. Poison ivy will not leave scars, unless a bacterial infection is involved.
Wet, cold compresses can soothe and relieve inflammation after the blisters have broken. Calamine lotion may relieve itching and acts as a drying agent.
In severe cases, corticosteroids (cortisone) may be recommended by a physician (either topically - directly on the skin - when a small area is involved, or by mouth if a larger area is affected).
Immunotherapy (allergy injections administered over time to increase tolerance) has not been proven effective as treatment. Avoidance is the best medicine.
What metals cause contact dermatitis?
Nickel, chrome and mercury are the most common causes of contact dermatitis. Nickel can be found in costume jewelry, belt buckles, and wristwatches as well as zippers, snaps and hooks on clothing. Since most commercial metals like chrome contain nickel, it is likely that contact with objects that are chrome-plated also will cause skin reactions in people sensitive to nickel.
Other causes of contact dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis can also be caused by personal care products such as make-up, hair products, face creams, nail polish, body lotions, sunscreen, as well as clothing, jewelry, medicine, rubber, chemicals, cleaning supplies and industrial-manufacturing products.
Metal allergy to surgical implants.
We frequently see patients referred usually by orthopedic surgeons to our office with a history of metal allergy prior to implant surgery. These metals usually consist of nickel, cobalt and chromium. By Patch testing these patients we can predict whether or not they might react to the metal implants after surgery to prevent any complications.
How do you diagnose contact dermatitis?
The gold standard for identification of contact allergens is Patch Testing.
What is patch testing?
Three tapes, which contain the most common contact allergens, are applied to the back and left for 48 hours, at which time they are removed and the test is read. In case of a positive reaction, the skin will turn red and in severe cases, it will even form a blister. Some patients have a delayed reaction on Patch testing; therefore the Patch test has to be read in 72-96 hours.






